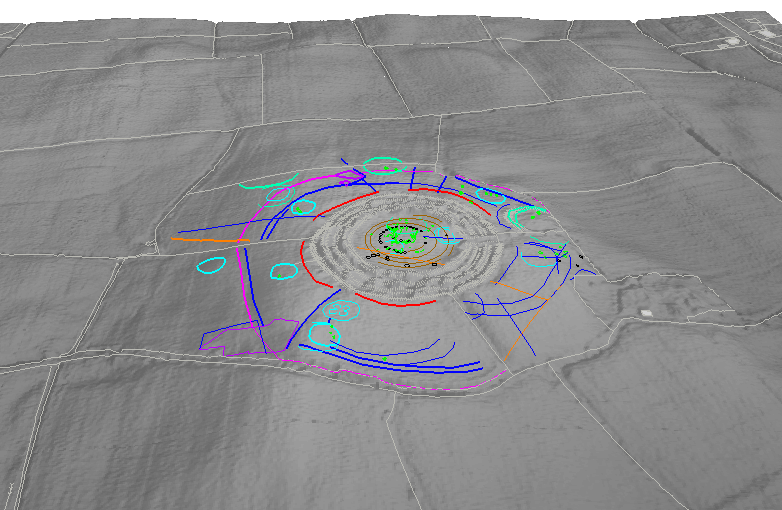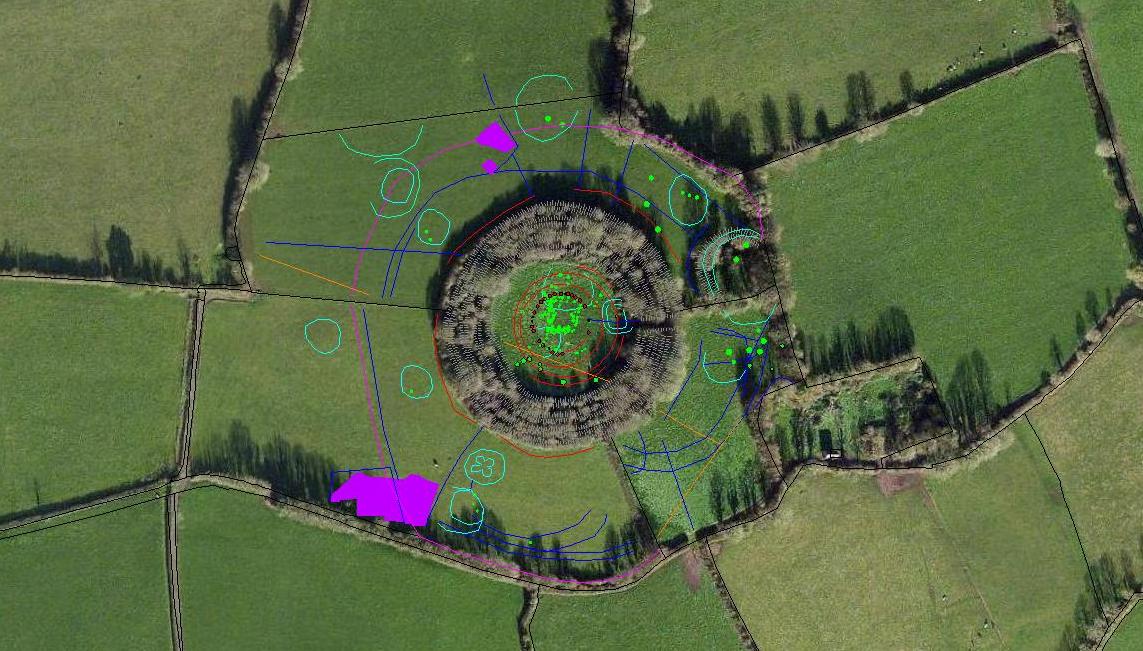
Combined geophysical survey results overlaid onto aerial photograph of Rathnadrinna, Cashel, Co. Tipperary
Project: Rathnadrinna Research Project, Cashel, Co. Tipperary.
Year: 2009-2014
Client: Richard O’Brien, funded by the Heritage Council and the Royal Irish Academy.
Aim:
Rathnadrinna Fort is a multivallate hilltop enclosure in the townland of Lalor’s-Lot outside Cashel, Co. Tipperary. It is one of the most impressive of several hilltop enclosures surrounding Cashel. In 2009, a project lead by Richard O’Brien began to carry out extensive investigations of the fort in order to gain further understanding of the history of the site. These included documentary research, aerial photographs, geophysical surveys and LiDAR. Earthsound were involved in the geophysical and LiDAR investigations of the enclosure and surrounding lands. The results of this research led up to a series of archaeological excavations lasting three seasons from 2012-2014.
Community Engagement:
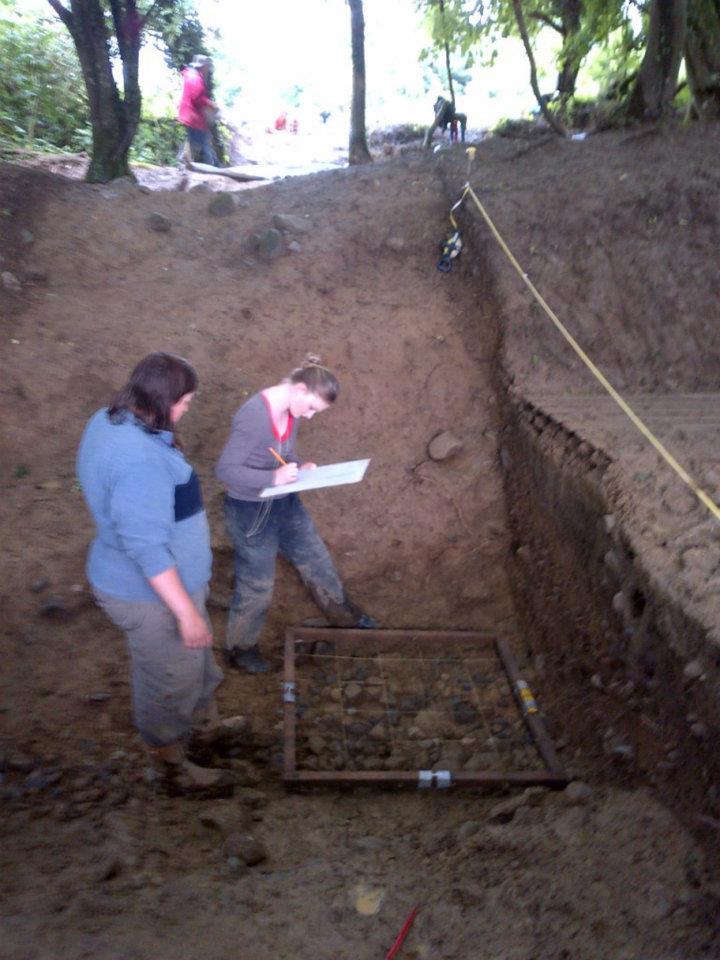
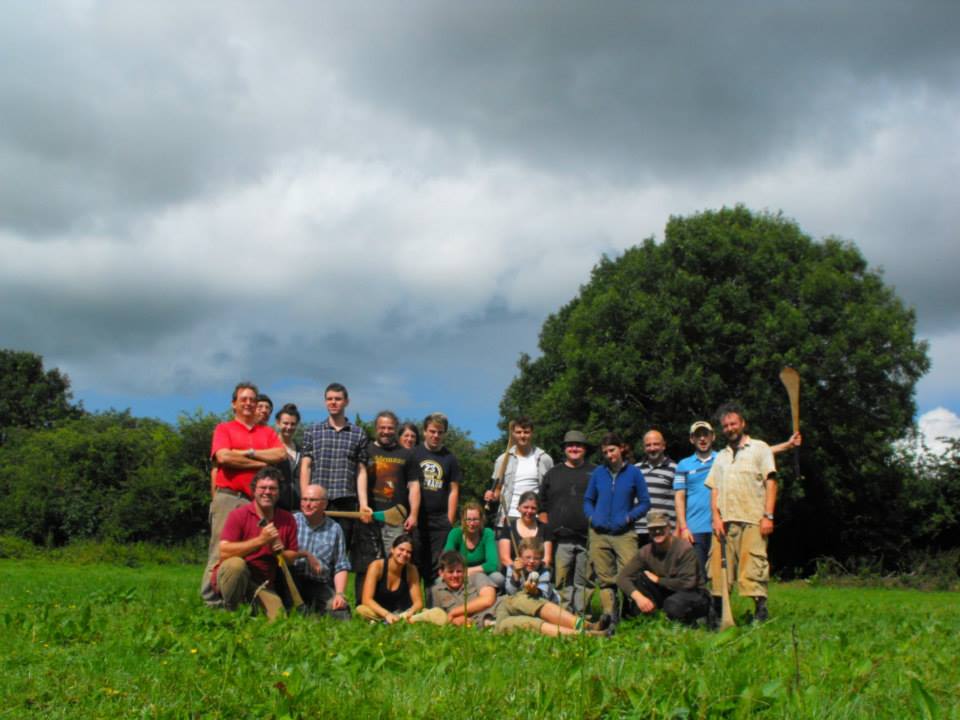
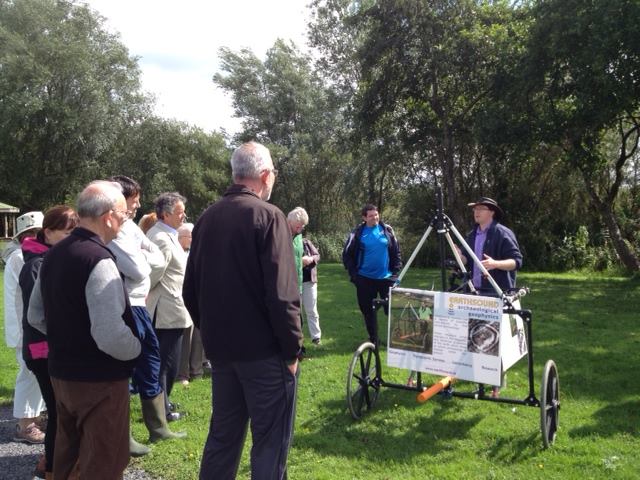
The Rathnadrinna Research project engaged members of the public throughout many of it’s stages. Locals and volunteers from all across the country and abroad were invited to join in the excavation team and be part of the project. Earthsound carried out a number of demonstrations of various geophysical techniques on site and some of the digging crew and visitors were able to get some hands on experience in operating the equipment.
Geophysics: In 2009 we carried out high resolution magnetic susceptibility, magnetometry, earth resistance and ground penetrating radar surveys within Rathnadrinna Fort and in a surrounding field. The magnetic susceptibility and magnetometry data suggest an absence of occupation and industry inside Rathnadrinna, which could suggest by default a ceremonial or ritual role for the fort. Evidence for a (presumably prehistoric) field system which pre-dates the construction of Rathnadrinna was also found. Parts of the field system may be fossilised in the extant field boundaries of today and also hint towards a larger outer enclosure, also partly preserved in the modern field boundaries. The earth resistance survey identified 3 further circular enclosing ditches within Rathnadrinna fort and 1 possible ditch beyond the fort in Field 1, as well as a pit-circle at the centre of the fort. These suggest that Rathnadrinna may have been comprised of 6 concentric ditches (3 of which are extant), and a possible 7th ditch on the exterior. Combining this data with a potential larger outer enclosure comprised of extant outer field boundaries surrounding Rathnadrinna, suggests that possibly up to 8 circular enclosing features may have been identified.
In 2010 further geophysical surveys were carried out including high resolution magnetic susceptibility, magnetometry and earth resistance and electrical resistivity tomography surveys. A number of linear and curvilinear ditches and possible ditches or gullies have been detected across the survey area. Many of these appear to be associated with relict field boundaries. 19th century activity was also identified in the form of two possible structural remains which match features on the 1st edition OS map. The hilltop of Rathnadrinna is surrounded by an enclosure ditch measuring 250m in diameter. This single ditch enclosed the top of the hillside and has influenced the arcing nature of some of the modern field boundaries. A large number of circular ring-ditches and arcing ditches have also been detected outside the known fort. These appear to fall into two distinct types based on their size and morphology. Small ring-ditches measuring 15m-19m in diameter may represent foundation slot-trenches or drip gullies surrounding (unrecorded) wooden structures. Larger circular features measuring 40m in diameter, similar to the upstanding remains of the known satellite fort beside Rathnadrinna. These anomalies may therefore represent possible ploughed-out ringforts. The magnetic susceptibility data suggests an absence of burning activity – like inside the fort – perhaps discounting a settlement role for the ring-ditches and ringforts indicating that they might be burial or ritual monuments.
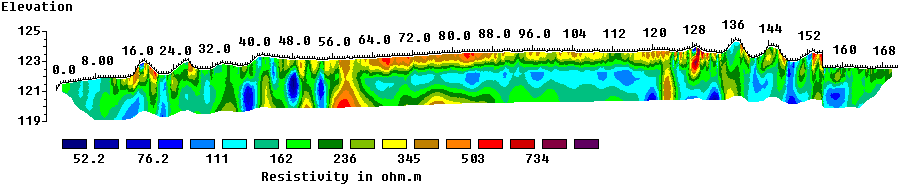
Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) line running S-N across the monument including all banks and ditches.
Excavation:
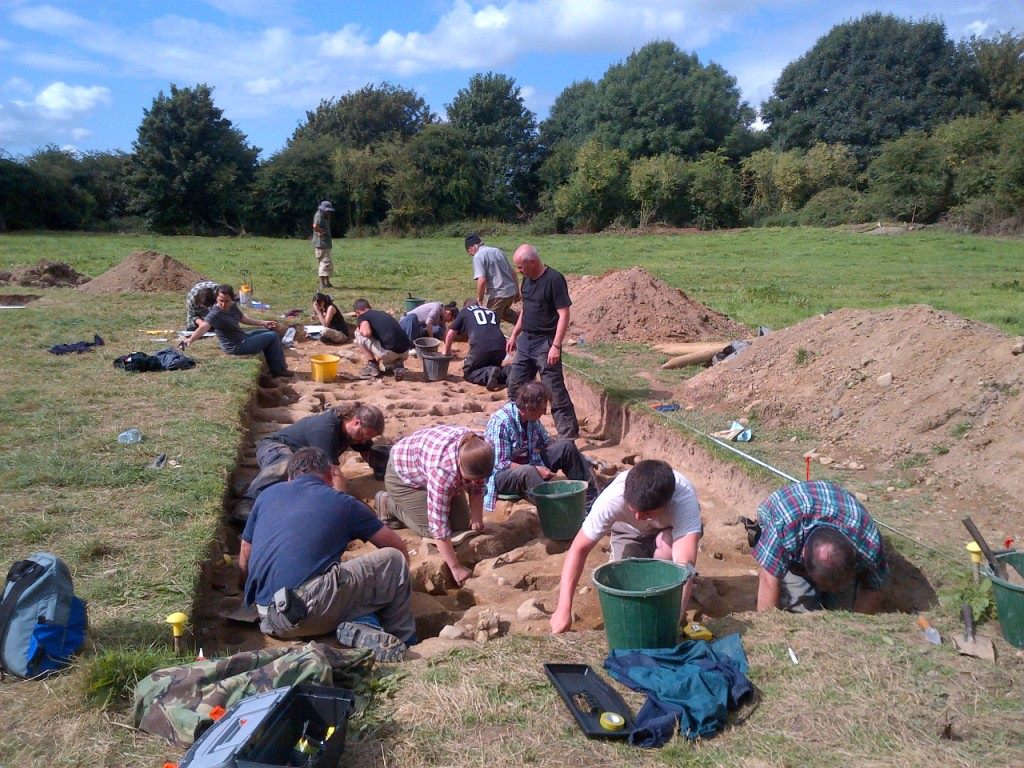
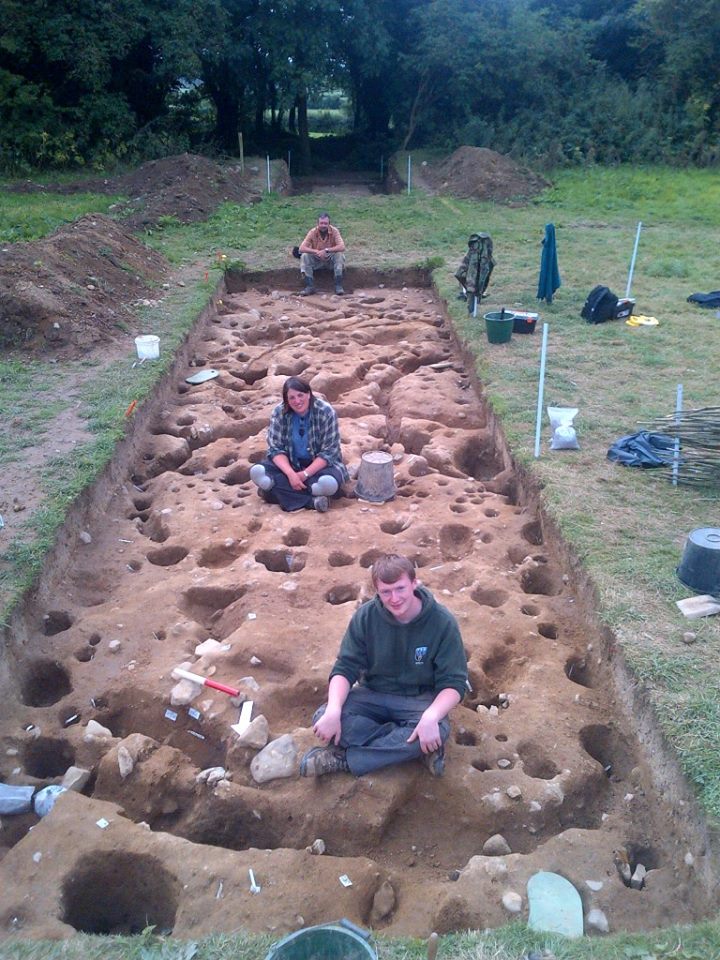
Three seasons of excavations, beginning in June 2012 and the final season concluding in August of 2014, were directed by Richard O’Brien. Earthsound’s Heather Gimson was part of the digging crew as archaeological supervisor throughout all of the excavations. Additional Geophysical data was collected and demonstrations of the survey techniques were carried out by our staff on several occasions during the excavation seasons.